MoE 原理及实现
Published:
MoE:mix of experts
- 专家 stack 起来,计算 token 经过每个专家的输出,对结果加权。
##
- 模型规模时提示性能的关键之一,有限的计算资源,用更少的训练步数训练一个更大的模型,通常比用更多步数训练小模型效果更佳。
- MoE 显著优势:
- 在远少于稠密模型所需计算资源下进行有效预训练。意味着在相同计算资源下,可以扩大模型或数据集规模。
- 特别是在预训练阶段,与稠密模型相比,混合专家模型通常能够更快地达到相同的质量水平。
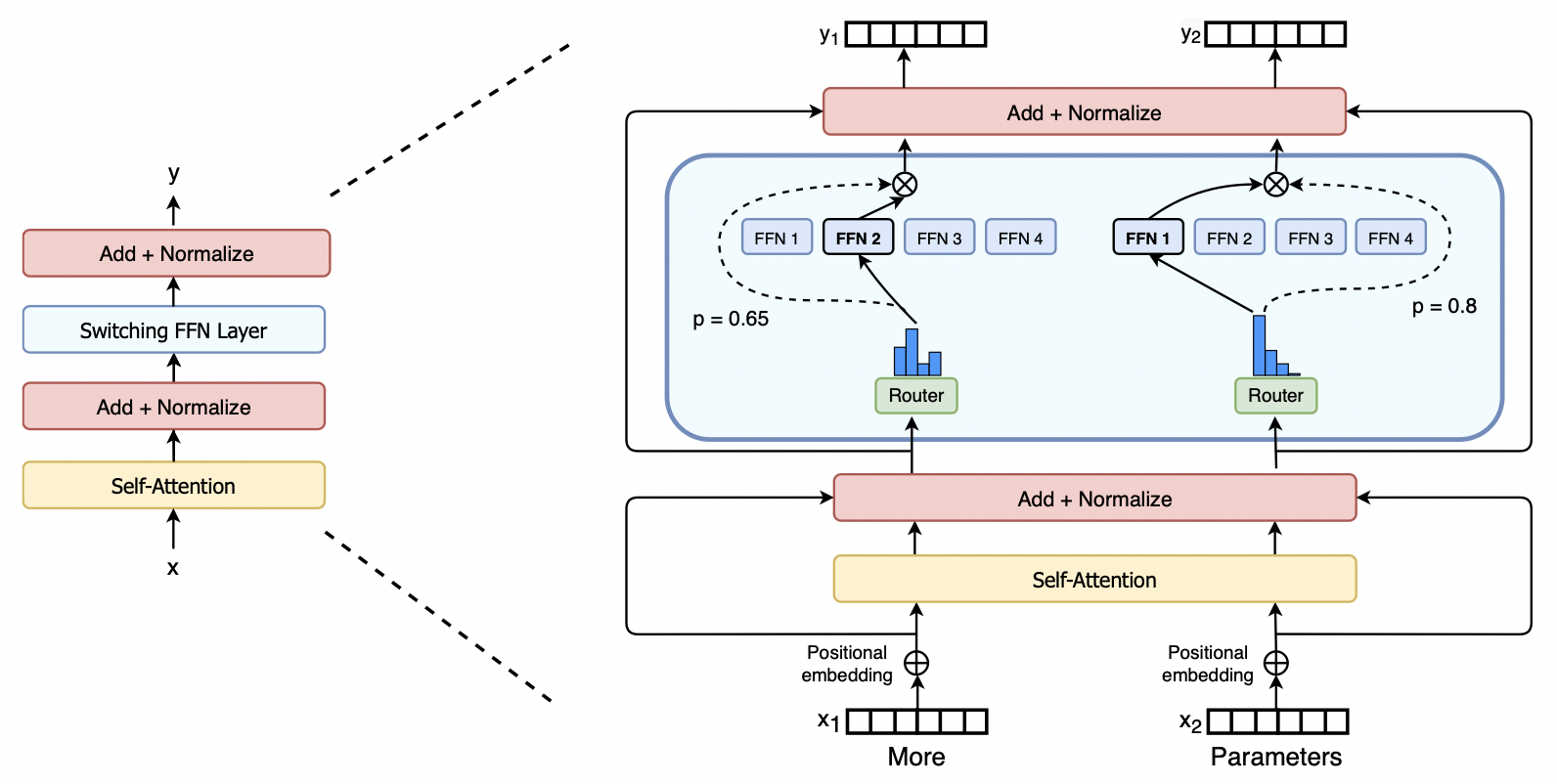
- 一句话:计算每个专家的输出,对结果加权。
- gate 实现:输入是 [batch_size, in_features],经过几个专家模型后把输出在 dim=1 维度上叠起来,得到 [batch_size, num_experts, out_features]。gate_score 维度变为 [batch_size, 1, num_experts],最后用 torch.bmm 计算所有专家输出的加权和,去掉中间那维,得到[batch_size, out_geatures]。
混合专家模型
- 专家模型(ffn) + 门控机制
- 最大特点:做了一个特征的增广,并且因为门控机制,能够在特征增广的同时,不会导致神经网络过拟合(门控机制保持了稀疏性)
- 用门控机制选择 token 到底通过哪一个ffn,或者说是按某种比例选择 ffn 进行学习。
- 门控决定哪些 token 被发送到哪个专家。类似集成学习思路,四个小的学习器汇成一个更强大的特征学习器
代码实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Expert(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features):
super(Expert, self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc(x)
return x
class MoELayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, num_experts):
super(MoELayer, self).__init__()
self.experts = nn.ModuleList(
[
Expert(in_features, out_features)
for _ in range(num_experts)
]
)
self.gate = nn.Linear(in_features, num_experts)
def forward(self, x):
gate_score = F.softmax(self.gate(x), dim=-1)
expert_output = torch.stack([expert(x) for expert in self.experts], dim=1)
out = torch.bmm(gate_score.unsqueeze(1), expert_output).squeeze(1)
return out