论文阅读: GPT-1.0
Published:
读 GPT-1.0 | 通过生成式预训练来提高语言理解
[TOC]
题目:Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training
作者:
链接:
代码:
推荐阅读:
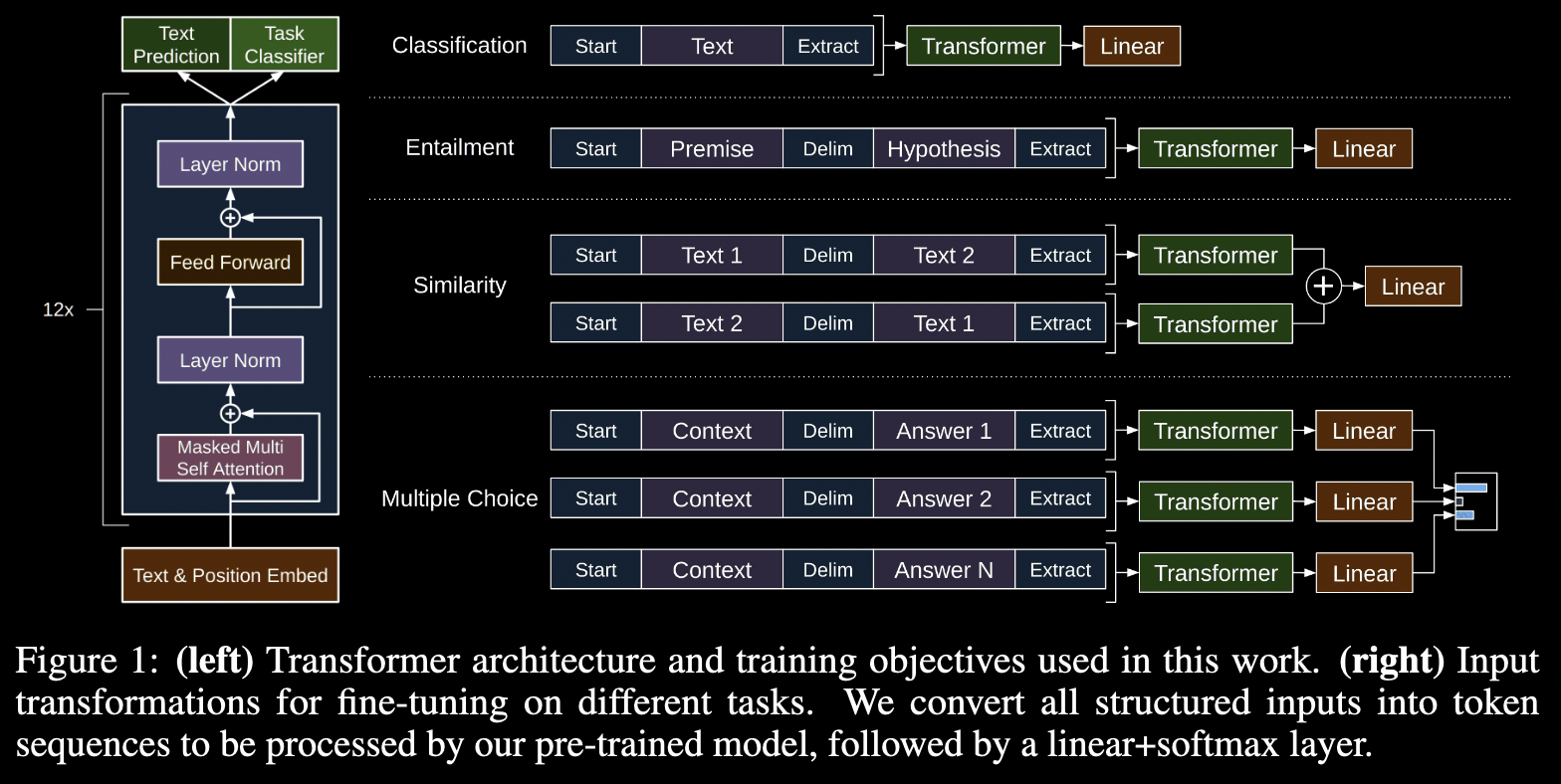
What:
- 数据量有问题:无标签的文本语料很多,但专门任务上的有标签数据很少,所以针对特定任务的模型表现不一定好。
- 解决方法:
- 用大量无标签的语料,通过生成式预训练,针对语言模型,然后在特定任务上进行针对性微调 discriminative fine-tuning。
- 和过去方法不同,在微调时,使用任务感知的输入变换取得高效 transfer,同时最小程度上修改模型架构。
读前问题:
Introduction
减轻对有监督学习的依赖,关键是从无标签的大量 raw text 中高效学习。就算有大量标签数据,用无监督的方式学特征也可以提高性能,例如 pretrained word embeddings。(首段说明无监督的重要性)
- 从无标签文本中,得到更多除了单词层面之外的信息(比如语义),有两大难点:
- 选什么优化目标才对迁移最有帮助。例如:language modeling,machine translation,discourse coherence。
- 怎样把学好的特征迁移到目标任务才是 most effective。例如:改模型架构(针对任务),更复杂的学习方案,加额外的辅助优化目标。 这些不确定性使得构建高效的半监督学习方法很困难。
- 探索了对于语言理解任务的半监督方法,包括无监督的预训练,和有监督的微调。目标是学到一个可以迁移适应大部分任务的通用特征。数据包括两部分,一个大型的无标签文本语料库,和几个人工标注的目标任务数据集。训练也分两步:
- 在无标签数据上用 language modeling objective 学到神经网络的初始化参数
- 用相应的 supervised objective 在目标任务上 adapt 这些参数。
模型结构上选用了 Transformer,在多个任务上表现出色,且能更好处理 long-term dependencies in text,因此迁移更鲁棒。在迁移上,用了特定任务的 adaptation,把 text 处理成 token sequence,因此对于预训练模型的结构上只用做最小程度的改变。
- 在四种语言理解任务上评价:natural language inference, question answering, semantic similarity, text classification。甚至比这种针对特定任务改特定架构的模型性能更好。还分析了 zero-shot behaviors,表明预训练模型确实具备下游任务的语言知识。
Related Work
NLP 的半监督学习
无监督预训练:目的是找到一个好的初始化点,而不是改目标函数。之前的研究表明,预训练作为一种正则化方案,使神经网络有更强的泛化性。
其他人的工作要么用RNN,不能捕捉到 long-range 的 lingustic structure,要么需要在下游任务重新训练一个模型,没本文的改动少。辅助训练的 objectives:没那么关键。
Framework:
训练分两步:
- 在一个大型的 text corpus 上学到 high-capacity 的语言模型
- fine-tuning stage:在有标签数据的特定任务上微调
1. Unsupervised pre-training
- 目标函数:standard language modeling objective。即整个 sequence 的条件概率。
- 模型:只用了 Transformer decoder:多头自注意力和按位置的前向层。
2. Supervised fine-tuning
- 目标函数:把无监督预训练好的参数用于目标任务,输入是 token 序列,输出是 transformer 最后一层的激活经过线性层分类头,和softmax,预测标签 y。优化目标就是分类损失 softmax loss,即 -log(正确类别的概率)。
- 辅助 loss:在微调任务中也加上 language modeling 损失,有助于提高有监督模型泛化能力,加速收敛。
- 微调任务中额外参数只有最后一层用于分类的线性层,和 delimiter 标识符 的 token embeddings。
3. Task-specific input transformations
- 下游的文本分类任务无需改变输入token的形式
- 但 question answering,textual entailment 这类任务需要输入是固定结构,例如 sentence pairs,或者三元组:document, question, answers。
- 过去的做法是改模型结构,但本任务把固定输入转为预训练模型可以处理的有序 token sequence,从而避免模型结构的改变。
All transformations include adding randomly initialized start and end tokens (〈s〉, 〈e〉).
- Textual entailment: premise +
<$>+ hypothesis - Similarity: 按前后顺序跑两遍,把得到的两个特征 sequence 相加
- QA 和 Commonsense Reasoning: 一个问题一般有许多回答,context + question +
<$>+ N * answers。每个答案跑一遍,最后用 softmax 归一化,得到一个所有可能答案的输出分布。
实验:
1. 设置
无监督预训练
用 BooksCorpus 数据集,关键在于长连续句,有助于学到长距离信息。模型 \
| GPT | Transformer | |
|---|---|---|
| Positonal encoding | learnable | sinusoidal(mainstream) |
| num_attention_heads | 12 | 8 |
| num_hidden_layers | 12 | 6 encoder layers, 6 decoder layers |
| hidden_size | 768 | 512 |
| vocab_size | 40478 | depends on dataset |
| FFN path |
|
|
- 超参数
- Optimizer: Adam, max_lr = 2.5e-4, 经过 2000 次更新从 0 线性增加,最终余弦退火到 0。
- Batch_size = 64
- epoch = 100
- max_seq_len = 512
- init_weight = N(0, 0.02)
- BPE_merges = 40000
- dropout = 0.1
- weight_decay = 0.01,不对 bias 和 gain weights做正则
- 和 vanilla transformer 的主要区别
- Decoder only (with causal mask)
- hidden_size = 768
- attention_heads = 12
- 因为是预训练模型,固定了 vocab_size
- GELU (Gaussian Error Linear Unit)
- learned position embeddings
- normalization:ftfy library
- tokenizer:spaCy
- Fine-tuning:
- 最终分类器也加了 dropout
- lr = 6.25e-5
- batchsize = 32
- epoch = 3
- lr_decay:线性,warmup 占训练的 0.2%
- λ = 0.5
分析:
Impact of number of layers transferred
增加一个迁移的层能提高 9% 性能。Zero-shot Behaviors \
- 为了更好的理解为什么预训练有效。一个假设是,基本的生成式模型因为学到评估任务,来提高语言建模能力。
- 因此不用有监督微调,只用预训练,性能也很好。
总结:
- 引入了一个框架,实现更强的自然语言理解能力。用单一模型,通过生成式预训练和有区别的微调。
- 通过在不同长连续文本语料库上的预训练,使模型获得了world knowledge和处理长距离依赖的能力,并成功迁移到了特定任务上。
- 本工作展示了无监督预训练和针对性微调这一流程的可行,提供了模型(Transformers)和数据集(text with long range dependencies)选取的建议。
- 最后强调无监督学习。
代码 code review
- 预训练任务做的是 language modeling,本质是 next word prediction,无监督的没有gt,为的就是省去额外的人工处理,可以不需要 special tokens(例如在 bookcorpus 上的预训练)。在 SST-2 数据集上微调时,由于后续要做推理,因此预处理时加上了special tokens,并做padding。(预训练不用特殊词元,下游任务微调时才加上)
- 为什么说用的是 decoder 的部分呢?encoder 和 decoder 的区别在于:encoder 能看到整个序列,decoder 有 mask,只能看到他自己和之前位置上的一部分。
- 为什么自注意力的方式 QK 是自己乘自己呢?(其实是为了做多头?)本质上是因为想要并行化计算整个句子的条件概率分布,为了以二维矩阵的形式用 decoder mask。比如,
NLP,训练时单纯用逐个输入的方式(也可以看成是 mask 掉后面部分),第一次输入N,第二次NL,第三次NLP,来计算新的去掉 mask 的位置对于它前面的所有位置的有序序列的依赖关系(即序列建模问题中,每个位置上的条件概率)(但是注意力计算不用考虑顺序,P 先和 N 还是 先和 L 算注意力不重要)。如果是用这种一维的 mask 实现,本质上还是串行,每次输入加上逐步右移的mask。那总结一下,一维的 mask 只能串行,那如果用二维下三角的 mask 矩阵呢?是不是能并行,那我的输入是什么形式才能用上这个二维的 mask 矩阵?答案呼之欲出,需要同时有两个输入,让输入序列乘上它自己。 - 微调过程输入是右移的gt:
<start>+ seq,目标是 seq +<extract>,本质上还是在做 language modeling,原始logits大小为[B, seq_len, d_model]。经过 lm_head 后输出格式为 [B, seq_len, vocab_size]。即最终返回的 hidden_states 和 lm_logits。 - 这里4说法不对,hidden_states 大小为 [B, seq_len, d_model],经过 lm_head 后得到 lm_logits,大小为 [B, seq_len, vocab_size]。微调时,只用了 hidden_states 的最后一个 token,hidden_states[:, -1],即特殊词元
<extract>,作为整句话的特征提取,经过分类头 clf_head 后得到 clf_logits。最终微调 loss 由 clf_logits 和 lm_logits 两部分构成。 - hidden_states 经过下游任务的 clf_head 得到 clf_logits,微调过程的整体 loss 由 clf_logits 和 lm_logits 两部分构成。
- 推理过程:切片取输出最后一个 token 的 logits(未归一化的特征表示),并除以 temperature 控制随机性:
logits = logits[:, -1, :] / temperature,后续取 top_k,然后做 softmax 得到前k的概率分布,最后用torch.multinomial从概率分布中随机采样。 - 为什么对bookcorpus和SST-2的预处理方式不一样,因为前者没有标签,就是用于无监督预训练的,无需人工额外处理。后者有标签,作为微调任务的评价指标,因此先加了start,extract,然后做BPE的encode,最后用rnn.pad_sequence做了padding,
pad_idx重用了unk的,都为0。 - Bookcorpus 作为无监督预训练数据集,不需要预处理,不用考虑padding,直接按 max_len 截断: ``` text { “text”: “But I traded all my life for some lovin’ and some gold” }
7. SST-2 作为下游情感分类任务 "negative" (0) or positive (1):
``` text
{'idx': 0,
'sentence': 'hide new secretions from the parental units ',
'label': 0}
- Q:有个很困惑的问题,由于pad是加在end后的,也就是说做翻译任务的 vanilla transformer 不是在训练什么时候该输出结尾end,因为最后一个 token 其实是 pad,不是 end。因为整个 batch 内要按最长的句子补0,而pad_idx 只是为了做 attention mask,计算注意力时不考虑 padding 部分,那最终 tgt 的输出不是还有 padding吗,因为翻译任务的 gt 也在预处理的时候补 0 了。
进入 tokenizer 前的预处理:
<start> hide new secretions from the parental units <extract>
<start> goes to absurd lengths <extract> <pad> <pad> <pad>
- A:实际上 padding 并不参与训练,从两方面实现:
- attention 都 mask 掉了 padding,每个 token 都和补0无关。
- loss 也 mask 掉了 padding,仅计算有效 token 的预测损失。
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss( ignore_index=tgt_tokenizer.token_to_id(PAD_TOKEN), label_smoothing=config.eps_ls )
- A:训练过程,并非逐词预测,而是并行处理整个序列,一次性预测所有位置的词。通过 decoder mask 实现。
- 输入输出结构:训练时,目标序列已知,decoder 的输入是右移的目标序列(例如
<sos> I love NLP),模型需要预测完整的序列(I love NLP <eos>),通过一次前向传播预测所有位置的token。 - 并行化实现:通过 decoder mask 屏蔽未来位置的信息,强制模型依赖历史信息。确保 Decoder 在预测每个位置时只能访问之前位置的信息,从而模拟自回归生成过程,但计算仍是并行的。
- 推理阶段才是逐词预测。
- 输入输出结构:训练时,目标序列已知,decoder 的输入是右移的目标序列(例如
- 表面上单纯看输入输出,是让模型学会何时输出停止符,但实际上,模型在每个位置上都在做 next word prediction,通过历史信息,并行预测目标序列的一部分(例如,通过
<sos> I预测I love,通过<sos> I love预测I love NLP,这都是并行的)。直接把目标序列作为gt,为了避免一步错步步错的情况。 - Teacher Forcing:在训练序列生成模型时使用。在每一步预测时,强制使用真实的前一个token作为输入,而非模型自身生成的词。
- 模型始终基于正确的上下文学习,加速模型收敛,提高训练稳定性。
- 可能导致模型过度依赖完美输入,在推理时(使用自身生成的词)表现下降(曝光偏差)。因为推理时早期预测错误会传播,模型没有学到纠错机制。
- 使用真实的目标序列作为 Decoder 输入,直接学习真实的上下文与目标词的映射关系。这样每一步的输入都来自真实数据,而非模型预测结果,避免错误累积。
- 缓解曝光偏差的方法:1.计划采样(Scheduled Sampling),逐步混合gt和模型预测输入。例如,训练初期全用gt,后期按概率替换为模型生成。2.强化学习(RL),引入奖励机制(如 BLEU,ROUGE),直接优化推理阶段的生成质量。
BPE
"""
bpe is short for Byte Pair Encoder. It translates arbitrary utf-8 strings into
sequences of integers, where each integer represents small chunks of commonly
occuring characters. This implementation is based on openai's gpt text_utils.py:
https://github.com/openai/finetune-transformer-lm/blob/master/text_utils.py
"""
import re
from typing import List, Optional, Union
import ftfy
import json
import spacy
from tqdm import tqdm
def get_pairs(word):
"""
Return all bigrams as a set of tuples, of consecutive elements in the iterable word.
"""
pairs = set()
prev_char = word[0]
for char in word[1:]:
pairs.add((prev_char, char))
prev_char = char
return pairs
def text_standardize(text):
"""
fixes some issues the spacy tokenizer had on books corpus
also does some whitespace standardization
"""
text = text.replace("—", "-")
text = text.replace("–", "-")
text = text.replace("―", "-")
text = text.replace("…", "...")
text = text.replace("´", "'")
# add spaces around all punctuations (-, ~, !, ", ;, ?, +, `,`, ), (, \, /, *, [, ], }, {, |, _)
# example: "Hi!Kami-chanw" will be converted to "Hi ! Kami - chanw"
text = re.sub(
r"""(-+|~+|!+|"+|;+|\?+|\++|,+|\)+|\(+|\\+|\/+|\*+|\[+|\]+|}+|{+|\|+|_+)""",
r" \1 ",
text,
)
# shrink spaces (or add spaces if not space exists) around `\n`
# exmaple: "Hi\nKamichanw \n" will be converted to "Hi \n Kamichanw \n "
text = re.sub(r"\s*\n\s*", " \n ", text)
# replace all space characters (e.g. `\t`) except `\n` with a single space
# exmaple: "Hi\tKamichanw \n" will be converted to "Hi Kamichanw \n "
text = re.sub(r"[^\S\n]+", " ", text)
return text.strip()
class BPETokenizer(object):
"""
mostly a wrapper for a public python bpe tokenizer
"""
def __init__(self, encoder_path, bpe_path):
self.nlp = spacy.load(
"en_core_web_sm",
disable=["parser", "tagger", "ner", "textcat", "lemmatizer"],
)
self.encoder = json.load(open(encoder_path))
self.decoder = {v: k for k, v in self.encoder.items()}
merges = open(bpe_path).read().split("\n")[1:-1]
merges = [tuple(merge.split()) for merge in merges]
self.bpe_ranks = dict(zip(merges, range(len(merges))))
self.cache = {}
self.special_tokens = {"</w>"}
def add_special_tokens(self, new_tokens: List[str]):
start_idx = len(self.encoder)
for i, token in enumerate(new_tokens):
if token in self.encoder:
raise ValueError(f"Token '{token}' already exists in the encoder.")
self.encoder[token] = start_idx + i
self.decoder[start_idx + i] = token
# no need to update BPE ranks for special tokens as they are not merged
self.cache[token] = token
self.special_tokens.update(new_tokens)
def get_vocab_size(self):
return len(self.encoder)
def bpe(self, token):
word = tuple(token[:-1]) + (token[-1] + "</w>",)
if token in self.cache:
return self.cache[token]
pairs = get_pairs(word)
if not pairs:
return token + "</w>"
while True:
# find the next lowest rank bigram that can be merged
# the lower rank means earlier be merged
bigram = min(pairs, key=lambda pair: self.bpe_ranks.get(pair, float("inf")))
if bigram not in self.bpe_ranks:
break # no more bigrams are eligible to be merged
first, second = bigram
# we will now replace all occurences of (first, second) in the list of current
# words into one merged token first_second, in the output list new_words
new_word = []
i = 0
while i < len(word):
# find the next occurence of first in the sequence of current words
try:
j = word.index(first, i)
new_word.extend(word[i:j])
i = j
except:
new_word.extend(word[i:])
break
# if this occurence is also followed by second, then merge them into one
if word[i] == first and i < len(word) - 1 and word[i + 1] == second:
new_word.append(first + second)
i += 2
else:
new_word.append(word[i])
i += 1
# all occurences of (first, second) have been merged to first_second
new_word = tuple(new_word)
word = new_word
if len(word) == 1:
break
else:
pairs = get_pairs(word)
word = " ".join(word)
if word == "\n </w>":
word = "\n</w>"
self.cache[token] = word
return word
def token_to_id(self, token: str) -> int:
return self.encoder.get(token, 0)
def encode(
self,
texts: Union[str, List[str]],
verbose: bool = True,
) -> List[List[int]]:
if not isinstance(texts, list):
texts = [texts]
texts_tokens = []
bar = tqdm(texts, ncols=80, leave=False) if verbose else texts
for text in bar:
text = self.nlp(text_standardize(ftfy.fix_text(text)))
text_tokens = []
for token in text:
text_tokens.extend(
[
self.encoder.get(t, 0)
for t in self.bpe(token.text.lower()).split(" ")
]
)
texts_tokens.append(text_tokens)
return texts_tokens
def decode(
self, bpe_idx: Union[List[List[int]], List[int]], skip_special_tokens=True
):
"""lists of integers comes in, a list of string comes out"""
if not isinstance(bpe_idx[0], list):
bpe_idx = [bpe_idx]
texts = []
for idx in bpe_idx:
# inverse map the integers to get the tokens
tokens_merged = [self.decoder[token] for token in idx]
text = "".join(tokens_merged)
if skip_special_tokens:
text = re.sub("|".join(self.special_tokens), " ", text)
texts.append(text)
return texts
Layers
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, num_attention_heads, max_len, dropout):
super().__init__()
assert hidden_size % num_attention_heads == 0
# key, query, value projections for all heads, but in a batch
self.c_attn = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 3 * hidden_size)
# output projection
self.c_proj = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size)
# regularization
self.attn_dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.resid_dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.dropout_prob = dropout
# flash attention make GPU go brrrrr but support is only in PyTorch >= 2.0
self.flash = hasattr(torch.nn.functional, "scaled_dot_product_attention")
# causal mask to ensure that attention is only applied to the left in the input sequence
self.register_buffer(
"bias",
torch.tril(torch.ones(max_len, max_len, dtype=torch.bool)).view(
1, 1, max_len, max_len
),
)
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
B, T, C = (
x.size()
) # batch size, sequence length, embedding dimensionality (hidden_size)
# calculate query, key, values for all heads in batch and move head forward to be the batch dim
q, k, v = self.c_attn(x).split(self.hidden_size, dim=2)
k = k.view(
B, T, self.num_attention_heads, C // self.num_attention_heads
).transpose(
1, 2
) # (B, nh, T, hs)
q = q.view(
B, T, self.num_attention_heads, C // self.num_attention_heads
).transpose(
1, 2
) # (B, nh, T, hs)
v = v.view(
B, T, self.num_attention_heads, C // self.num_attention_heads
).transpose(
1, 2
) # (B, nh, T, hs)
# causal self-attention; Self-attend: (B, nh, T, hs) x (B, nh, hs, T) -> (B, nh, T, T)
casual_mask = self.bias[:, :, :T, :T]
if mask is not None:
casual_mask = casual_mask & mask
if self.flash:
# efficient attention using Flash Attention CUDA kernels
y = F.scaled_dot_product_attention(
q,
k,
v,
attn_mask=casual_mask,
dropout_p=self.dropout_prob if self.training else 0,
)
else:
# manual implementation of attention
att = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * (1.0 / math.sqrt(k.size(-1)))
att = att.masked_fill(casual_mask == 0, float("-inf"))
att = F.softmax(att, dim=-1)
att = self.attn_dropout(att)
y = att @ v # (B, nh, T, T) x (B, nh, T, hs) -> (B, nh, T, hs)
y = (
y.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(B, T, C)
) # re-assemble all head outputs side by side
# output projection
y = self.resid_dropout(self.c_proj(y))
return y
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, num_attention_heads, max_len, dropout):
super().__init__()
self.ln_1 = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
self.attn = Attention(
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_attention_heads=num_attention_heads,
max_len=max_len,
dropout=dropout,
)
self.ln_2 = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
self.mlp = nn.ModuleDict(
dict(
c_fc=nn.Linear(hidden_size, 4 * hidden_size),
act=nn.GELU(approximate="tanh"),
c_proj=nn.Linear(4 * hidden_size, hidden_size),
dropout=nn.Dropout(dropout),
)
)
m = self.mlp
self.mlpf = lambda x: m.dropout(m.c_proj(m.act(m.c_fc(x))))
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
x = x + self.ln_1(self.attn(x, mask))
x = x + self.ln_2(self.mlpf(x))
return x
GPT
import inspect
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from .layers import Block
class GPT(nn.Module):
"""GPT Language Model"""
def __init__(
self,
vocab_size,
max_len,
hidden_size,
num_attention_heads,
num_hidden_layers,
dropout,
):
super().__init__()
self.max_len = max_len
self.transformer = nn.ModuleDict(
dict(
tokens_embed=nn.Embedding(vocab_size, hidden_size),
positions_embed=nn.Embedding(max_len, hidden_size),
drop=nn.Dropout(dropout),
h=nn.ModuleList(
[
Block(
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_attention_heads=num_attention_heads,
max_len=max_len,
dropout=dropout,
)
for _ in range(num_hidden_layers)
]
),
)
)
self.lm_head = nn.Linear(hidden_size, vocab_size, bias=False)
self.transformer.tokens_embed.weight = (
self.lm_head.weight
) # https://paperswithcode.com/method/weight-tying
# init all weights
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def get_num_params(self, non_embedding=True):
"""
Return the number of parameters in the model.
For non-embedding count (default), the position embeddings get subtracted.
The token embeddings would too, except due to the parameter sharing these
params are actually used as weights in the final layer, so we include them.
"""
n_params = sum(p.numel() for p in self.parameters())
if non_embedding:
n_params -= self.transformer.positions_embed.weight.numel()
return n_params
def _init_weights(self, module):
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
torch.nn.init.normal_(module.weight, mean=0.0, std=0.02)
if module.bias is not None:
torch.nn.init.zeros_(module.bias)
elif isinstance(module, nn.Embedding):
torch.nn.init.normal_(module.weight, mean=0.0, std=0.02)
elif isinstance(module, nn.LayerNorm):
torch.nn.init.zeros_(module.bias)
torch.nn.init.ones_(module.weight)
def configure_optimizers(
self, lr, weight_decay, betas=(0.9, 0.999), device_type=None
):
# start with all of the candidate parameters
# filter out those that do not require grad
param_dict = {pn: p for pn, p in self.named_parameters() if p.requires_grad}
# create optim groups. Any parameters that is 2D will be weight decayed, otherwise no.
# i.e. all weight tensors in matmuls + embeddings decay, all biases and layernorms don't.
decay_params = [p for n, p in param_dict.items() if p.dim() >= 2]
nodecay_params = [p for n, p in param_dict.items() if p.dim() < 2]
optim_groups = [
{"params": decay_params, "weight_decay": weight_decay},
{"params": nodecay_params, "weight_decay": 0.0},
]
num_decay_params = sum(p.numel() for p in decay_params)
num_nodecay_params = sum(p.numel() for p in nodecay_params)
print(
f"num decayed parameter tensors: {len(decay_params)}, with {num_decay_params:,} parameters"
)
print(
f"num non-decayed parameter tensors: {len(nodecay_params)}, with {num_nodecay_params:,} parameters"
)
# Create AdamW optimizer and use the fused version if it is available
fused_available = "fused" in inspect.signature(torch.optim.AdamW).parameters
use_fused = fused_available and device_type == "cuda"
extra_args = dict(fused=True) if use_fused else dict()
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(optim_groups, lr=lr, betas=betas, **extra_args)
print(f"using fused AdamW: {use_fused}")
return optimizer
@classmethod
def from_pretrained(
cls, model_name_or_path: str, num_frozen_layers=0, **gpt_kwargs
):
"""
Loads pretrained from transformers library.
Args:
model_name_or_path (str):
Can be "openai-gpt", "openai-community/openai-gpt", or a path to checkpoint directory,
which is same as `PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`.
num_frozen_layers (int):
The number of layers whose parameters need to be frozen. If it is not 0,
then the `num_frozen_layers` GPT blocks close to the input will be frozen,
that is, requires_grad=False.
gpt_kwargs:
The key-word args that passed to initialize GPT
"""
from transformers import OpenAIGPTLMHeadModel
default_config = dict(
vocab_size=40478,
max_len=512,
hidden_size=768,
num_attention_heads=12,
num_hidden_layers=12,
dropout=0.1,
)
default_config.update(gpt_kwargs)
model = cls(**default_config)
# report number of parameters
print("number of parameters: %.2fM" % (model.get_num_params() / 1e6,))
sd = model.state_dict()
sd_keys = sd.keys()
sd_keys = [
k for k in sd_keys if not k.endswith(".attn.bias")
] # discard this mask / buffer, not a param
# init a huggingface/transformers model
model_hf = OpenAIGPTLMHeadModel.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
model_hf.resize_token_embeddings(default_config["vocab_size"])
sd_hf = model_hf.state_dict()
# copy while ensuring all of the parameters are aligned and match in names and shapes
sd_keys_hf = sd_hf.keys()
ignored_suffix = [
".attn.bias", # buffer
".attn.masked_bias", # mask
]
sd_keys_hf = [
k
for k in sd_keys_hf
if all(not k.endswith(suffix) for suffix in ignored_suffix)
] # ignore these
# basically the openai checkpoints use a "Conv1D" module, but we only want to use a vanilla Linear
# this means that we have to transpose these weights when we import them
transposed = [
"attn.c_attn.weight",
"attn.c_proj.weight",
"mlp.c_fc.weight",
"mlp.c_proj.weight",
]
for k in sd_keys_hf:
if any(k.endswith(w) for w in transposed):
# special treatment for the Conv1D weights we need to transpose
assert sd_hf[k].shape[::-1] == sd[k].shape
with torch.no_grad():
sd[k].copy_(sd_hf[k].t())
else:
# vanilla copy over the other parameters
assert sd_hf[k].shape == sd[k].shape
with torch.no_grad():
sd[k].copy_(sd_hf[k])
layers_to_frozen = range(num_frozen_layers)
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
param.requires_grad = not any(f"h.{i}." in name for i in layers_to_frozen)
return model
def forward(self, input, input_mask=None, return_hiden_states=False):
device = input.device
b, t = input.size()
assert (
t <= self.max_len
), f"Cannot forward sequence of length {t}, block size is only {self.max_len}"
pos = torch.arange(0, t, dtype=torch.long, device=device) # shape (t)
# forward the GPT model itself
tok_emb = self.transformer.tokens_embed(
input
) # token embeddings of shape (b, t, hidden_size)
pos_emb = self.transformer.positions_embed(
pos
) # position embeddings of shape (t, hidden_size)
x = self.transformer.drop(tok_emb + pos_emb)
if input_mask is not None and input_mask.dim() == 2:
# [batch_size, seq_len] -> [batch_size, 1, 1, seq_len]
input_mask = input_mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2)
for block in self.transformer.h:
x = block(x, input_mask)
if return_hiden_states:
return self.lm_head(x), x
else:
return self.lm_head(x)
@torch.no_grad()
def generate(self, idx, max_new_tokens, temperature=1.0, top_k=None):
"""
Take a conditioning sequence of indices idx (LongTensor of shape (b,t)) and complete
the sequence max_new_tokens times, feeding the predictions back into the model each time.
Most likely you'll want to make sure to be in model.eval() mode of operation for this.
1. 如果序列长度超出最大,截断
2. 如果输出有两个,取第一个
3. 得到最后一个token的logits,并控制温度
4. 取 logits 的 top-k
5. softmax 归一化得到前k概率分布
6. 从中随机采样
7. 新的 next word 合并到原输入序列
"""
for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
# if the sequence context is growing too long we must crop it at max_len
idx_cond = idx if idx.size(1) <= self.max_len else idx[:, -self.max_len :]
# forward the model to get the logits for the index in the sequence
logits = self(idx_cond)
# only take the first output, i.e. lm_logits
if isinstance(logits, (tuple, list)):
logits = logits[0]
# pluck the logits at the final step and scale by desired temperature
logits = logits[:, -1, :] / temperature
# optionally crop the logits to only the top k options
if top_k is not None:
v, _ = torch.topk(logits, min(top_k, logits.size(-1)))
logits[logits < v[:, [-1]]] = -float("inf")
# apply softmax to convert logits to (normalized) probabilities
probs = F.softmax(logits, dim=-1)
# sample from the distribution
idx_next = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1)
# append sampled index to the running sequence and continue
idx = torch.cat((idx, idx_next), dim=1)
return idx
class GPTClassifier(GPT):
def __init__(
self,
n_classes,
vocab_size,
max_len,
hidden_size,
num_attention_heads,
num_hidden_layers,
dropout,
):
super().__init__(
vocab_size,
max_len,
hidden_size,
num_attention_heads,
num_hidden_layers,
dropout,
)
self.clf_head = nn.Linear(hidden_size, n_classes, bias=False)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, input, input_mask=None):
lm_logits, hidden_states = super().forward(
input, input_mask=input_mask, return_hiden_states=True
)
clf_logits = self.clf_head(self.dropout(hidden_states[:, -1]))
return lm_logits, clf_logits
data
from math import ceil
from typing import Sequence
import datasets
from datasets import DownloadManager
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from torch.nn.utils.rnn import pad_sequence
import config
from modules.bpe import BPETokenizer
SOS_TOKEN = "<start>"
CLF_TOKEN = "<extract>"
special_tokens = [SOS_TOKEN, CLF_TOKEN]
pad_idx = 0 # reuse unk as pad token
class TokenIDDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_source, num_token_per_item: int):
"""
This class is used to read continuous max_len tokens from data_source.
Args:
data_source:
A BookCorpus dataset where each item contains token ids of a sentence.
num_token_per_item (int):
The number of token ids of an item.
"""
super().__init__()
self.data_source = data_source
self.num_token_per_item = num_token_per_item
def __getitem__(self, index):
rest_length = self.num_token_per_item
sequence = []
while rest_length > 0:
token_ids = self.data_source[index]["text"]
sequence.extend(token_ids[:rest_length])
rest_length -= len(token_ids)
index += 1
return torch.tensor(sequence, dtype=torch.long)
def __len__(self):
accumulate_length = 0
for i, example in enumerate(reversed(self.data_source)):
accumulate_length += len(example["text"])
if accumulate_length >= self.num_token_per_item:
return len(self.data_source) - i
return 0
def _load_bookcorpus(tokenizer, loading_ratio, num_proc, splits):
if not splits is None and splits != ["train"]:
raise ValueError('Splits must be ["train"] or None.')
def tokenize(example):
example["text"] = tokenizer.encode(example["text"], verbose=False)
return example
# 10 files in total, but we may just use part of them
URLS = [
f"https://hf-mirror.com/datasets/bookcorpus/bookcorpus/resolve/refs%2Fconvert%2Fparquet/plain_text/train/000{i}.parquet?download=true"
for i in range(ceil(loading_ratio * 10))
]
dl_manager = DownloadManager("bookcorpus")
paths = dl_manager.download(URLS)
print("Downloaded at ", paths)
# 74004228 rows in total, see https://huggingface.co/datasets/bookcorpus/bookcorpus
dataset = (
datasets.load_dataset(
"parquet", data_files=paths, split="train", num_proc=num_proc
)
.select(range(int(loading_ratio * 74004228)))
.map(tokenize, load_from_cache_file=True, num_proc=num_proc, batched=True)
)
return [
DataLoader(
TokenIDDataset(dataset, num_token_per_item=config.max_len),
batch_size=config.PretrainConfig.batch_size,
shuffle=True,
)
]
def _load_sst2(tokenizer: BPETokenizer, loading_ratio, num_proc, splits):
all_splits = ["train", "validation", "test"]
if splits is None:
splits = all_splits
elif not set(splits).issubset(all_splits):
raise ValueError(f"Splits should only contain some of {all_splits}")
tokenizer.add_special_tokens(special_tokens)
def collate_fn(batch):
sentences, labels = [], []
for item in batch:
sentences.append(SOS_TOKEN + item["sentence"] + CLF_TOKEN)
labels.append(item["label"])
tokens = tokenizer.encode(
sentences,
verbose=False,
)
tensors = [torch.tensor(tok, dtype=torch.long) for tok in tokens]
return pad_sequence(
tensors, batch_first=True, padding_value=pad_idx
), torch.tensor(labels, dtype=torch.long)
dataset = datasets.load_dataset("stanfordnlp/sst2", num_proc=num_proc)
dataloaders = []
for split in splits:
ds = dataset[split]
subset = ds.select(range(int(loading_ratio * len(ds))))
dataloaders.append(
DataLoader(
subset,
config.FinetuningConfig.batch_size,
collate_fn=collate_fn,
shuffle=split == "train",
)
)
return dataloaders
def load_data(
name: str,
loading_ratio: float = 1,
num_proc: int = 1,
splits: Sequence[str] = None,
):
dispatch = { # _load_* should return a list of dataloader
"bookcorpus": _load_bookcorpus,
"sst2": _load_sst2,
}
assert (
name.lower() in dispatch
), f"Unsupported dataset, should be one of {list(dispatch.keys())}"
assert 0 < loading_ratio <= 1
tokenizer = BPETokenizer(
config.bookcorpus_dir / "encoder_bpe_40000.json",
config.bookcorpus_dir / "vocab_40000.bpe",
)
return tokenizer, *dispatch[name.lower()](
tokenizer, loading_ratio, num_proc, splits
)
config
import os
from dataclasses import dataclass
from pathlib import Path
import torch
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = ",".join(
str(i) for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count())
)
torch.manual_seed(3407)
# model parameter setting
max_len = 512
hidden_size = 768
num_hidden_layers = 12
num_attention_heads = 12
vocab_size = 40478
dropout = 0.1
@dataclass
class PretrainConfig:
n_epoch = 100
batch_size = 16
accumulate_grad_batches = 4
lr = 2.5e-4
warmup_steps = 2000
@dataclass
class FinetuningConfig:
n_epoch = 3
batch_size = 32
accumulate_grad_batches = 1
lr = 6.25e-5
clf_loss_weight = 0.5
warmup_steps = 0.2 / 100
# path
base_dir = Path(__file__).parent.resolve()
checkpoint_dir = base_dir / "checkpoints"
bookcorpus_dir = base_dir / "datasets" / "bookcorpus"
# if you downloaded pretrained gpt in an automatical manner, set pretrained_dir to "openai-community/openai-gpt"
# otherwise, you can obtain pretrained model with huggingface-cli, see README.md appendix
pretrained_dir = checkpoint_dir / "gpt"
os.makedirs(checkpoint_dir, exist_ok=True)
# optimizer args
weight_decay = 1e-2
clip = 1
# inference
num_beams = 3
top_k = 30
top_p = 0.7
temperature = 1.0
length_penalty = 0.7
pretrain
import config
from data import load_data
import torch
from modules import GPT
from tqdm import tqdm
import torch.nn as nn
import os
from transformers import get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup
# only use 1% BookCorpus dataset
loading_ratio = 0.01
tokenizer, dataloader = load_data("bookcorpus", loading_ratio=loading_ratio, num_proc=5)
total_steps = (
len(dataloader) * config.PretrainConfig.n_epoch // config.PretrainConfig.accumulate_grad_batches
)
# scale warmup steps
warmup_steps = int(
config.PretrainConfig.warmup_steps
* loading_ratio
// config.PretrainConfig.accumulate_grad_batches
)
device = torch.device("cuda:1")
model = GPT(
vocab_size=config.vocab_size,
max_len=config.max_len,
hidden_size=config.hidden_size,
num_attention_heads=config.num_attention_heads,
num_hidden_layers=config.num_hidden_layers,
dropout=config.dropout,
).to(device)
def split_batch(batch):
src, tgt = batch[:, :-1], batch[:, 1:]
return src.to(device), tgt.to(device)
def train(epoch, model, criterion, optimizer, scheduler):
model.train()
total_loss = 0
step = 0
optimizer.zero_grad()
for batch in tqdm(dataloader, desc=f"Training Epoch {epoch}"):
src, tgt = split_batch(batch)
# [batch_size, max_len - 1, vocab_size]
outputs = model(src)
# [batch_size * (max_len - 1), vocab_size]
outputs = outputs.contiguous().view(-1, tokenizer.get_vocab_size())
loss = criterion(outputs, tgt.contiguous().view(-1))
loss.backward()
if (step + 1) % config.PretrainConfig.accumulate_grad_batches == 0 or (step + 1) == len(
dataloader
):
nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), config.clip)
optimizer.step()
scheduler.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
step += 1
total_loss += loss.item()
avg_loss = total_loss / len(dataloader)
return avg_loss
def training_loop(restore_epoch=-1):
optimizer = model.configure_optimizers(
lr=config.PretrainConfig.lr,
weight_decay=config.weight_decay,
device_type="cuda",
)
scheduler = get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup(
optimizer=optimizer,
num_training_steps=total_steps,
num_warmup_steps=warmup_steps,
)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
restore_ckpt_path = config.checkpoint_dir / f"gpt_{restore_epoch}.pth"
if restore_epoch != -1 and os.path.exists(restore_ckpt_path):
ckpt = torch.load(restore_ckpt_path)
assert ckpt["epoch"] == restore_epoch
model.load_state_dict(ckpt["model"])
optimizer.load_state_dict(ckpt["optimizer"])
scheduler.load_state_dict(ckpt["scheduler"])
else:
restore_epoch = 0
for epoch in range(restore_epoch, config.PretrainConfig.n_epoch):
avg_train_loss = train(epoch + 1, model, criterion, optimizer, scheduler)
print(
f"Epoch {epoch + 1}/{config.PretrainConfig.n_epoch}, Training Loss: {avg_train_loss: .4f}"
)
checkpoint_path = config.checkpoint_dir / f"gpt_{epoch + 1}.pth"
torch.save(
{
"epoch": epoch + 1,
"model": model.state_dict(),
"optimizer": optimizer.state_dict(),
"scheduler": scheduler.state_dict(),
},
checkpoint_path,
)
training_loop()