cs231n_1
Published:
CS231n: 1. Introduction & KNN & Data Split
太长不看
- 图像分类问题:将像素的集合,映射到标签。
- L1 距离:差的绝对值,求和
- L2 距离:欧式距离,差值的平方,求和,开根号
- 五折交叉:训练集分五份,一份轮流当验证集,取平均。用验证集选超参。
- 如果超参数多,倾向于用更大的验证集。但如果验证集很小,几百个左右,还是交叉验证更安全。
1. Image Classification
- Motivation
从一个固定类别中给图像分配标签。图像:[width, height, channel] 三维的亮度值数组。 - 例子
对于一个 [248, 400, 3] 的图像,该图像由 297600 个数字组成,每个数都是范围从 0(黑色)到 255(白色)的整数,任务是将这数十万个数字变成一个标签。 - 挑战
视角变化,大小,形变,遮挡,光照,背景干扰,类别内部差异。 模型要对类别内部变化不变,同时对类别间变化敏感。 - 数据驱动
教小孩:设计一个学习算法,给计算机提供每个类的许多例子,学到每个类的视觉外观。 - 流程
为图像(像素点数组)分配标签- 输入:训练集,由 N 个图像和对应 K 个标签组成
- 学习:从训练集学到每个类长什么样。
- 评估:预测没见过的新图像,和 gt 对比。
2. Nearest Neighbor Classifier
- CIFAR-10
[32, 32, 3] 小图像,一共 10 类。50,000 训练集,10,000 测试。 - 最近邻
将测试图像和训练集每个图像比较,选距离最近图像的标签。 L1 distance
对每个像素,差的绝对值求和
\(d_1(I1,I2)=∑_p∣∣I^p_1−I^p_2∣∣\)def predict(self, X): """ X is N x D where each row is an example we wish to predict label for """ num_test = X.shape[0] # lets make sure that the output type matches the input type Ypred = np.zeros(num_test, dtype = self.ytr.dtype) # loop over all test rows for i in range(num_test): # find the nearest training image to the i'th test image # using the L1 distance (sum of absolute value differences) distances = np.sum(np.abs(self.Xtr - X[i,:]), axis = 1) min_index = np.argmin(distances) # get the index with smallest distance Ypred[i] = self.ytr[min_index] # predict the label of the nearest exampleL2 distance
用 L1 CIFAR-10 ACC 38.6%,计算向量间欧式距离,差值平方根求和
\(d_2(I1,I2)=\sqrt{∑_p(I^p_1−I^p_2)^2}\)distances = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(self.Xtr - X[i,:]), axis = 1))根号可去掉,不影响。L2 CIFAR-10 ACC 35.4%
L2 prefers medium disagreements to big one
3. k - Nearest Neighbor Classifier (KNN)
- 在训练集中找前 k 个最接近的图像,对测试投票。较高 k 值有 smoothing effect,更能抵抗异常值,泛化性更好。
- k 选多少最好? 超参:k 值,距离选择,L1 or L2
4. Validation sets for Hyperparameter tuning
- 不要用测试集调参,否则就是将测试集作为训练集,去过拟合测试集。
Evaluate on the test set only a single time, at the very end. - 从训练集分出验证集。CIFAR-10: 49000 train, 1000 valid
Split your training set into training set and a validation set. Use validation set to tune all hyperparameters. At the end run a single time on the test set and report performance. - Cross-validation
场景:训练集和验证集很小。
5-fold cross-validation: 训练集分 5 份,4份训练,1份验证。迭代每个折作为验证集,取平均。
对于 k 近邻:每个 k 都跑 5 个值,取平均。 - In practice
实践中,倾向于使用 50% - 90% 作为训练集,剩余验证。如果超参数多,倾向于用更大的验证集。但如果验证集很小,几百个左右,还是交叉验证更安全。
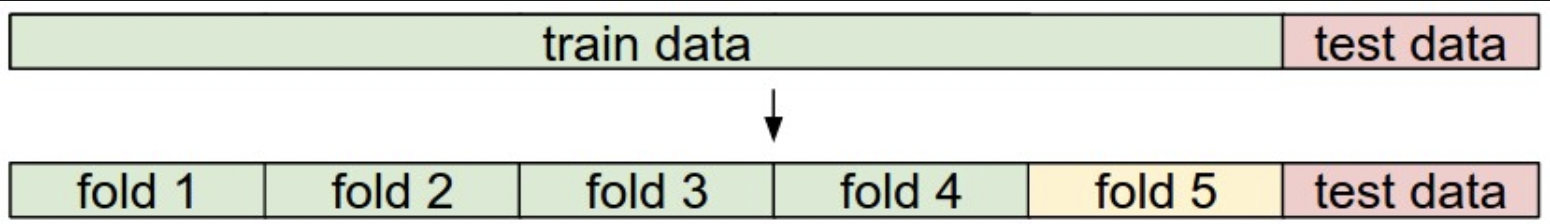
A training and test set is given. The training set is split into folds (for example 5 folds here). The folds 1-4 become the training set. One fold (e.g. fold 5 here in yellow) is denoted as the Validation fold and is used to tune the hyperparameters. Cross-validation goes a step further and iterates over the choice of which fold is the validation fold, separately from 1-5. This would be referred to as 5-fold cross-validation. In the very end once the model is trained and all the best hyperparameters were determined, the model is evaluated a single time on the test data (red).
5. 最近邻优缺点
- 训练无需时间,本质上是存储+索引。测试计算成本高,和深度网络相反。
- 对低维数据好用,图像分类不好用。图像的像素距离没有感知或语义。
- t-SNE 将图像嵌入到 2 维,保留 pairwise distances,计算 L2 距离,相似的图像是背景接近的,或颜色分布,而不是语义。
- 在原始像素值上使用 L1 或 L2 距离是不够的,因为距离与背景和颜色分布更相关,而不是图像的语义内容。
6. KNN 应用
- 数据预处理:归一化特征,例如图像中的一个像素点。均值 0,方差 1。但图像中的像素通常是同质化的,分布不会有很大不同,减轻了归一化需要。
- 如果数据维度很高,考虑降维:PCA,NCA,Random Projection
- 训练数据划分训练集验证集。一般训练集 70% - 90%。如果超参多,使用更大的验证集。最好交叉验证。
- 选 k 和 距离计算方式。
总结
- 引入了图像分类问题:将像素的集合,映射到标签。
- L1 距离:差的绝对值,求和
- L2 距离:欧式距离,差值的平方,求和,开根号
- 五折交叉:训练集分五份,一份轮流当验证集,取平均。用验证集选超参。
- 如果超参数多,倾向于用更大的验证集。但如果验证集很小,几百个左右,还是交叉验证更安全。