重读经典: ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Published:
读 CACM17 | AlexNet 使用深度卷积神经网络进行 ImageNet 分类
题目:ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
作者:Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, Geoffrey E. Hinton
链接:https://papers.nips.cc/paper_files/paper/2012/file/c399862d3b9d6b76c8436e924a68c45b-Paper.pdf
代码:https://github.com/dansuh17/alexnet-pytorch
推荐阅读: AlexNet论文逐段精读【论文精读】https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ih411J7Kz/?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0
AlexNet论文精读及模型详解 https://www.zhihu.com/tardis/bd/art/681432892
卷积神经网络经典回顾之AlexNet https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/618545757
【卷积神经网络-进化史】从LeNet到AlexNet https://www.zhihu.com/column/p/21562756
手撕 CNN 经典网络之 AlexNet https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/467017218
AlexNet网络结构详解 https://blog.csdn.net/guzhao9901/article/details/118552085
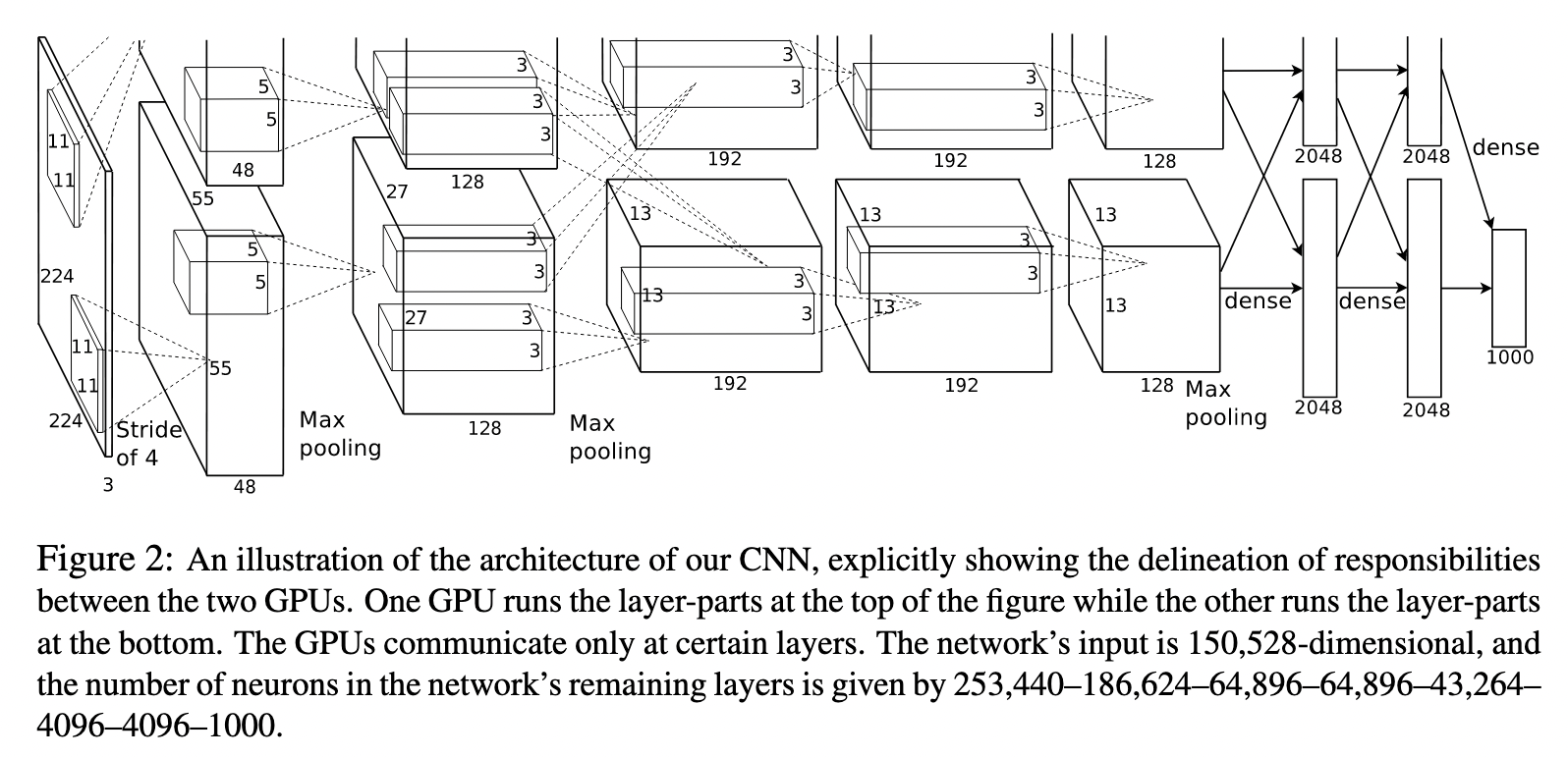
What:
- 新结构:更深的 LeNet + ReLU + MaxPooling: 5 * conv + 3 * fc
- 防过拟合:DataAugmentation + dropout
- GPU 并行
- 数据量增大,需要更强学习能力的模型。但大数据集也无法应对复杂的目标识别问题,因此需要先验知识来弥补缺少的数据。CNN 假设图像具有局部依赖性和平移不变性,相比 ffn 参数量更少,易于训练。
读前问题:
- 每层的参数为什么这样设计
- 图像数据增强,预处理方法?(答:短边缩放到 256,裁剪中央 256 * 256 的块。预处理:减去训练集均值。
- 特征可视化?(答:全连接最后一层 4096 维特征计算欧氏距离
- 训练设置?(答:SGD,batch_size = 128, momentum = 0.9, weight_decay = 0.0005
We initialized the weights in each layer from a zero-mean Gaussian distribution with standard deviation 0.01. We initialized the neuron biases in the second, fourth, and fifth convolutional layers, as well as in the fully-connected hidden layers, with the constant 1. This initialization accelerates the early stages of learning by providing the ReLUs with positive inputs. We initialized the neuron biases in the remaining layers with the constant 0.
We found that this small amount of weight decay was important for the model to learn. In other words, weight decay here is not merely a regularizer: it reduces the model’s training error.
We used an equal learning rate for all layers, which we adjusted manually throughout training. The heuristic which we followed was to divide the learning rate by 10 when the validation error rate stopped improving with the current learning rate. The learning rate was initialized at 0.01 and reduced three times prior to termination. We trained the network for roughly 90 cycles through the training set of 1.2 million images, which took five to six days on two NVIDIA GTX 580 3GB GPUs.
How:
- ReLU 训练更快
主要是因为它是linear,而且 non-saturating(因为ReLU的导数始终是1),相比于 sigmoid/tanh,ReLU 只需要一个阈值就可以得到激活值,而不用复杂运算。
- cross-GPU parallelization:卷积核对半分,只在特定层交互,其他情况各训各的。
- Local Response Normalization:ReLU 不需要输入标准化,但是该操作有助于泛化。借鉴生物中的侧抑制原理,其实效果有限,没有也行。
- Overlapping Pooling:卷积核 3 * 3,步长 2. 更难过拟合。
- 总体架构:第三层卷积核两张卡一起训练,标准化在一二层卷积后,一二五层卷积后 Max-pooling。RuLU每层后都有。
- Data Augmentation:两种,第一种:random 224 * 224 + 水平翻转 –> 2048 倍,测试时从四个角和中心 crop 224 + 水平翻转,10 个 crop 取平均。作者说,不做随机crop,大网络基本都过拟合(under substantial overfitting)。第二种:对 RGB 空间做 PCA,然后对主成分做一个(0, 0.1)的高斯扰动。结果让错误率又下降了1%。
- Dropout:前两层全连接,p = 0.5。每次输入,神经网络对不同架构进行采样,训练时以概率 p 将每个神经元的输出设为 0,减少神经元之间的依赖性,迫使学到更 robust 的特征。测试时对所有神经元输出乘 p。
实验:
- ILSVRC-2010: top-1 error = 37.5%, top-5 = 17.0%
- Qualitative Evaluations: GPU1 的卷积核颜色无关,GPU2 的和颜色相关。包括频率,方向选择,色彩斑点
- visual knowledge:最后 4096 维的特征,欧氏距离说明相似性。也可以训练自编码器降到 2 维再计算相似度。无关语义相似,倾向于检索有相似边缘的图像。
总结:
- 模型参数量大 60 million parameters,即使1.2 million 数据也容易过拟合。
- 删掉单个卷积层,性能下降。
- 未来加无监督预训练
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
"""
Neural network model consisting of layers propsed by AlexNet paper.
"""
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):
"""
Define and allocate layers for this neural net.
Args:
num_classes (int): number of classes to predict with this model
"""
super().__init__()
# input size should be : (b x 3 x 227 x 227)
# The image in the original paper states that width and height are 224 pixels, but
# the dimensions after first convolution layer do not lead to 55 x 55.
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=96, kernel_size=11, stride=4), # (b x 96 x 55 x 55)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.LocalResponseNorm(size=5, alpha=0.0001, beta=0.75, k=2), # section 3.3
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # (b x 96 x 27 x 27)
nn.Conv2d(96, 256, 5, padding=2), # (b x 256 x 27 x 27)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.LocalResponseNorm(size=5, alpha=0.0001, beta=0.75, k=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # (b x 256 x 13 x 13)
nn.Conv2d(256, 384, 3, padding=1), # (b x 384 x 13 x 13)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 384, 3, padding=1), # (b x 384 x 13 x 13)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, 3, padding=1), # (b x 256 x 13 x 13)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # (b x 256 x 6 x 6)
)
# classifier is just a name for linear layers
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(in_features=(256 * 6 * 6), out_features=4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=True),
nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=num_classes),
)
self.init_bias() # initialize bias
def init_bias(self):
for layer in self.net:
if isinstance(layer, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.normal_(layer.weight, mean=0, std=0.01)
nn.init.constant_(layer.bias, 0)
# original paper = 1 for Conv2d layers 2nd, 4th, and 5th conv layers
nn.init.constant_(self.net[4].bias, 1)
nn.init.constant_(self.net[10].bias, 1)
nn.init.constant_(self.net[12].bias, 1)
def forward(self, x):
"""
Pass the input through the net.
Args:
x (Tensor): input tensor
Returns:
output (Tensor): output tensor
"""
x = self.net(x)
x = x.view(-1, 256 * 6 * 6) # reduce the dimensions for linear layer input
return self.classifier(x)
# define pytorch device - useful for device-agnostic execution
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# define model parameters
NUM_EPOCHS = 90 # original paper
BATCH_SIZE = 128
MOMENTUM = 0.9
LR_DECAY = 0.0005
LR_INIT = 0.01
IMAGE_DIM = 227 # pixels
NUM_CLASSES = 1000 # 1000 classes for imagenet 2012 dataset
DEVICE_IDS = [0, 1, 2, 3] # GPUs to use
# modify this to point to your data directory
INPUT_ROOT_DIR = 'alexnet_data_in'
TRAIN_IMG_DIR = 'alexnet_data_in/imagenet'
OUTPUT_DIR = 'alexnet_data_out'
LOG_DIR = OUTPUT_DIR + '/tblogs' # tensorboard logs
CHECKPOINT_DIR = OUTPUT_DIR + '/models' # model checkpoints
# make checkpoint path directory
os.makedirs(CHECKPOINT_DIR, exist_ok=True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# print the seed value
seed = torch.initial_seed()
print('Used seed : {}'.format(seed))
tbwriter = SummaryWriter(log_dir=LOG_DIR)
print('TensorboardX summary writer created')
# create model
alexnet = AlexNet(num_classes=NUM_CLASSES).to(device)
# train on multiple GPUs
alexnet = torch.nn.parallel.DataParallel(alexnet, device_ids=DEVICE_IDS)
print(alexnet)
print('AlexNet created')
# create dataset and data loader
dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(TRAIN_IMG_DIR, transforms.Compose([
# transforms.RandomResizedCrop(IMAGE_DIM, scale=(0.9, 1.0), ratio=(0.9, 1.1)),
transforms.CenterCrop(IMAGE_DIM),
# transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
]))
print('Dataset created')
dataloader = data.DataLoader(
dataset,
shuffle=True,
pin_memory=True,
num_workers=8,
drop_last=True,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
print('Dataloader created')
# create optimizer
# the one that WORKS
optimizer = optim.Adam(params=alexnet.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
### BELOW is the setting proposed by the original paper - which doesn't train....
# optimizer = optim.SGD(
# params=alexnet.parameters(),
# lr=LR_INIT,
# momentum=MOMENTUM,
# weight_decay=LR_DECAY)
print('Optimizer created')
# multiply LR by 1 / 10 after every 30 epochs
lr_scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=30, gamma=0.1)
print('LR Scheduler created')
# start training!!
print('Starting training...')
total_steps = 1
for epoch in range(NUM_EPOCHS):
lr_scheduler.step()
for imgs, classes in dataloader:
imgs, classes = imgs.to(device), classes.to(device)
# calculate the loss
output = alexnet(imgs)
loss = F.cross_entropy(output, classes)
# update the parameters
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# log the information and add to tensorboard
if total_steps % 10 == 0:
with torch.no_grad():
_, preds = torch.max(output, 1)
accuracy = torch.sum(preds == classes)
print('Epoch: {} \tStep: {} \tLoss: {:.4f} \tAcc: {}'
.format(epoch + 1, total_steps, loss.item(), accuracy.item()))
tbwriter.add_scalar('loss', loss.item(), total_steps)
tbwriter.add_scalar('accuracy', accuracy.item(), total_steps)
# print out gradient values and parameter average values
if total_steps % 100 == 0:
with torch.no_grad():
# print and save the grad of the parameters
# also print and save parameter values
print('*' * 10)
for name, parameter in alexnet.named_parameters():
if parameter.grad is not None:
avg_grad = torch.mean(parameter.grad)
print('\t{} - grad_avg: {}'.format(name, avg_grad))
tbwriter.add_scalar('grad_avg/{}'.format(name), avg_grad.item(), total_steps)
tbwriter.add_histogram('grad/{}'.format(name),
parameter.grad.cpu().numpy(), total_steps)
if parameter.data is not None:
avg_weight = torch.mean(parameter.data)
print('\t{} - param_avg: {}'.format(name, avg_weight))
tbwriter.add_histogram('weight/{}'.format(name),
parameter.data.cpu().numpy(), total_steps)
tbwriter.add_scalar('weight_avg/{}'.format(name), avg_weight.item(), total_steps)
total_steps += 1
# save checkpoints
checkpoint_path = os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_DIR, 'alexnet_states_e{}.pkl'.format(epoch + 1))
state = {
'epoch': epoch,
'total_steps': total_steps,
'optimizer': optimizer.state_dict(),
'model': alexnet.state_dict(),
'seed': seed,
}
torch.save(state, checkpoint_path)